

Aim to gradually reduce BP to the patient's estimated 95 th centile.

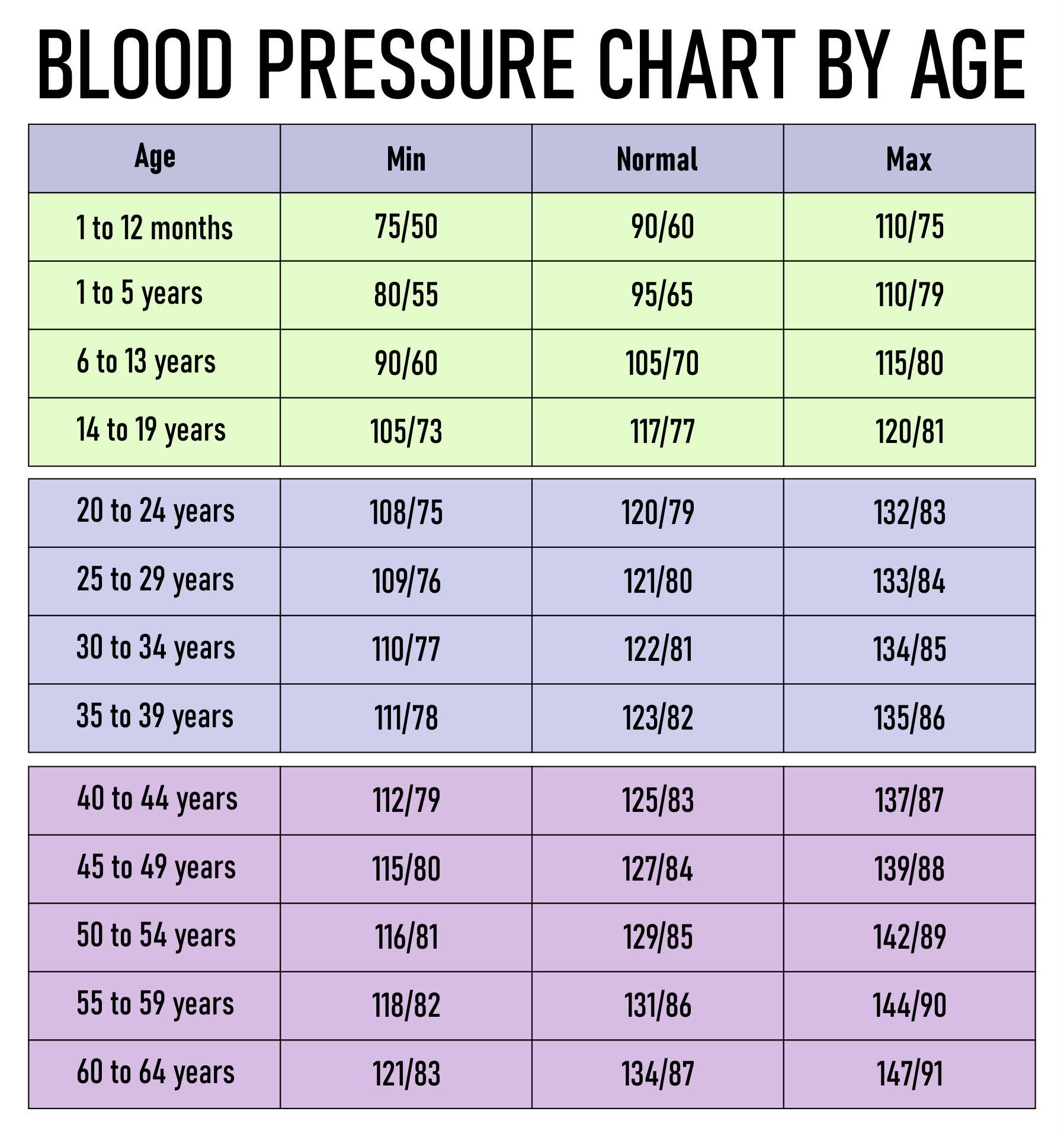
Primary/essential hypertension accounts for the majority of hypertension in children >6 years old and is generally associated with obesity or a family history of hypertension.Hypertension in childhood is a key predictor of risk for hypertension, cardiovascular disease and end organ damage in adulthood.This guideline will focus on the paediatric population aged 1–17 years (not infants).Where possible, abnormal machine BP measurement should be confirmed, preferably with a manual BP, ensuring appropriately sized cuff is used for accurate measurement.Blood pressure should be measured annually in healthy children.All hypertension in children requires monitoring and follow-up.Hypertension associated with encephalopathy is a medical emergency Severe hypertension requires urgent consultation and management.BP by age and height centile tables: boys girls Key points


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
